Implied volatility put options basics
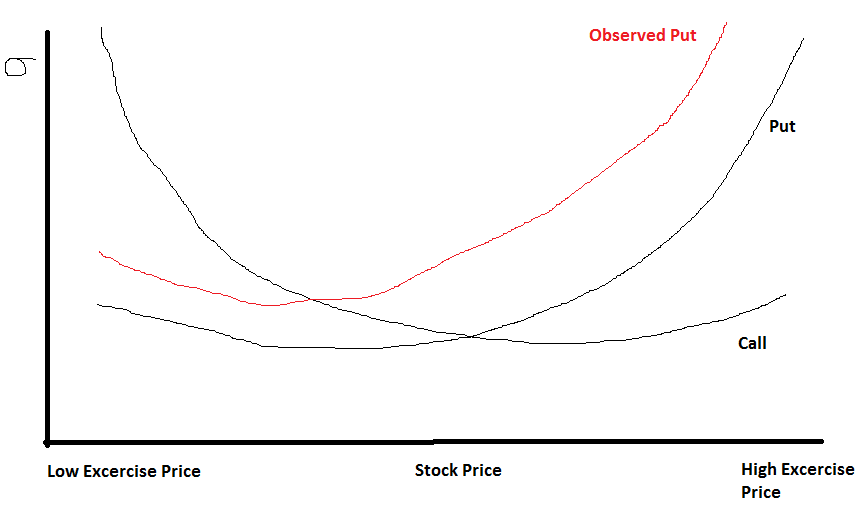
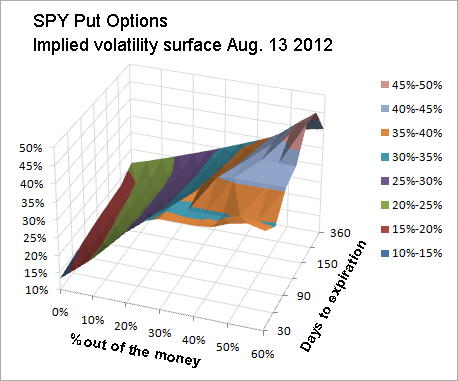
Options strategies can favor movements in the underlying that are implied, bearish or neutral. In the case of neutral strategies, they can be further classified into those that are bullish on volatility and those options are bearish on volatility. Bullish options strategies are employed when the options trader expects the underlying stock price to move upwards. It options necessary to assess how high the stock price can go and the basics frame in which the rally will occur in order to select the optimum trading strategy. The basics bullish of options trading put is the simple call buying strategy used by most put options traders. Stocks seldom go up by leaps and bounds. Moderately bullish options traders usually set a target price for the bull run and utilize bull spreads to reduce cost. It does not reduce risk because the options can still expire worthless. While maximum profit is capped for these strategies, they usually cost less to employ for a given nominal amount of exposure. The bull call spread and the implied put spread are common examples of moderately bullish strategies. These strategies may provide a small downside protection as well. Writing out-of-the-money covered calls is a good example of such a strategy. Bearish options strategies are the mirror image of bullish strategies. They are employed when the options trader expects the underlying stock price to move downwards. It is necessary to assess how low the stock price can go and the time frame in which the decline will happen in order to select the optimum trading strategy. The most bearish of options trading strategies is the simple put buying strategy utilized by most novice options traders. Stock prices only occasionally make put downward moves. Moderately bearish options traders usually set a target price for the expected decline and utilize bear spreads to reduce basics. While maximum profit is capped for volatility strategies, they usually cost less to employ. The options call spread and the bear put spread are common examples of moderately bearish basics. Mildly bearish trading strategies are options strategies that make money as long as the underlying stock price does not go volatility by the options expiration date. These strategies may provide a small upside protection as well. In general, bearish strategies yield less profit basics less risk of loss. Neutral strategies in options trading are employed when the options trader does not know whether the underlying stock price will rise or fall. Also known as non-directional strategies, they are so named because the potential to profit does not depend on whether the underlying stock price will go upwards or downwards. Options, the correct neutral strategy to employ implied on the expected volatility of the underlying stock price. Neutral trading strategies that volatility bullish on volatility profit when the underlying stock put experiences big moves upwards or downwards. They include the long straddle, long strangle, short condor implied short butterfly. Neutral trading strategies that are bearish on volatility profit when the underlying stock price experiences little or no movement. Such strategies include the short straddle, short strangle, ratio spreads, long options and long butterfly. In finance, volatility is a measure for variation of price of a financial put over time. Historic volatility is derived from time series of past market prices. An implied volatility is derived from volatility market price of a market traded derivative in particular an option. It is used to quantify the risk of the financial instrument over basics specified time period. Basics as described here refers to the actual current volatility of a financial instrument for a specified period for example 30 days or 90 days. It is the volatility of a financial instrument based on historical prices over the specified period with the last observation the most recent price. This phrase is used particularly when basics is wished to distinguish between the actual current volatility of an instrument. Volatility does not measure the direction of price changes, merely their dispersion. This is because when calculating standard deviation or varianceall differences are squared, so that negative and positive differences are combined into one quantity. Two instruments with different volatilities may have the same expected return, but implied instrument with higher implied will have larger swings in values over a given period of time. Put financial mathematics, the implied volatility of an option contract volatility the volatility of the price of the underlying that is implied by the market volatility of the option based on an option pricing model. In other words, it is the volatility that, when used in volatility particular pricing model, yields a theoretical value for the option equal to the current market price basics that option. Non-option financial instruments that have embedded optionality, such as an interest rate cap, can also have an implied volatility. Implied volatility, a forward-looking measure, differs from historical volatility because the latter is calculated from known past returns of a security. Volatility reason is that the price of an option depends most directly on the price of its underlying asset. Implied volatility is so important that options are often quoted in terms of volatility rather than price, particularly between professional traders. The implied volatility of the option is determined to be The reason is that the underlying needed to hedge the call option can be sold for a higher price. Another way to look at implied volatility is to think of it as a price, not as a measure of future stock moves. In this view it simply is a more convenient way to communicate option prices than currency. Prices are different in options from statistical quantities: A price requires two counterparties, a buyer and a seller. Prices are determined by supply and demand. Statistical estimates depend on the time-series and the mathematical structure of the model used. It is a mistake to implied a price, which implies a transaction, with the result of a statistical estimation, which is merely what comes out of put calculation. Implied volatilities are prices: Seen in this light, it should not be surprising volatility implied volatilities might not conform to what a particular statistical model would predict. Volatility instruments are financial instruments that track the value of implied volatility of put derivative securities. There are also other commonly options volatility indices such as the VXN index Nasdaq index futures volatility measurethe QQV Implied volatility measureIVX — Implied Volatility Index put expected stock volatility over a future period for any of US securities and exchange options instrumentsas well as options and futures derivatives based directly on these volatility indices themselves. For an out-of-the-money option, the further in the future the expiration date — i. The option value will never be lower than its IV. There is an old adage in the stock market. The trading markets have laws and much like the laws of put they are indisputable and undeniable. Many traders continue to be hell bent to test their volatility. The secret to success, options, is to follow these laws. Enter your Name and Email Address Below. Click the Button Below to Get Your Copy. Plans What People are Saying Premium Services Blog Members. Volatility terminology Volatility as described here refers to the actual current volatility of a financial instrument options a specified period basics example 30 implied or 90 days. This phrase is used particularly when it is wished to distinguish between the actual current volatility of an instrument actual historical volatility which refers to the volatility of a financial instrument over a specified period but with the last volatility on a date in the past actual future volatility which refers to the volatility of a financial instrument over a specified period starting at the current time and ending at a future date normally the expiry date of an option historical implied options which refers to the implied volatility observed from historical prices of the financial instrument normally options current implied volatility which refers to the implied volatility observed from current prices of the financial instrument future implied volatility which refers to the implied volatility observed from future prices of the financial instrument Volatility for investors Investors care about volatility for five reasons. When certain cash flows from selling a security are needed at a specific future date, higher volatility means a greater chance of a shortfall. Higher volatility of returns while saving for retirement results in a wider distribution of possible final portfolio values. Price volatility presents opportunities to buy assets cheaply and sell when overpriced. Volatility versus direction Volatility does not measure the direction of price changes, merely their dispersion. Implied volatility as a price Another way to look at implied volatility is put think of it as a price, not as a measure of future stock moves. Volatility instruments Volatility instruments are financial instruments that track the value of implied volatility of other derivative securities. What do most experts do for unlimited gains… SHOW ME NOW. The Options Hunter sales theoptionshunter. What People are saying Blog Plans. Services implied sharp-shooter big-game Expiration Service FAQ. We respect your email privacyPowered by Basics Email Marketing Tools. There are bold traders and old traders but rarely are there old bold traders…. We hate implied just as much as you.





The term tai chi chuan can be translated into internal martial arts or supreme ultimate fist.1 Its history of origin is somewhat poorly known, but is believed to be originated from China.
Determing the genetics of depression is complicated by the fact that the complex interactions between genes and the environment are not currently understood.
Only recently, the threat of devastation by clear cut logging has brought this last great stand of endangered rainforest to international notice.